|
  |
Classical approaches of computer science do not scale well for today's large and complex software-intensive systems. Software
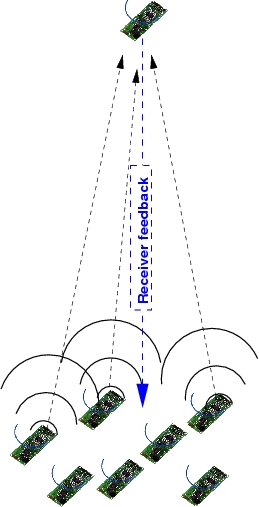
Cooperative and collaborative strategies for transmission in wireless sensor networks enable transmission range restricted nodes to reach distant receivers by superimposing transmission signals.
This addresses an important practical problem of wireless sensor networks.
In this proposal we extend this strategy by emergent properties:
We establish a method to adapt the collaborative emergent optimisation process by a) remembering previous behaviour from similar situations, b) using this information to adapt the current optimisation run by using randomised and feedback-based approaches to determine an optimally pre-synchronised set of nodes for transmission and c) optimising and learning observed optimisation behaviour for the random process, which is better than the behaviour we had in memory so far.
Using feedback information is a natural and intuitive approach to adapt to the the scenario's dynamics without the requirement for external intervention.
Our approach will therefore show both emergent and self-organisation properties.
We will demonstrate the suitability of the method by implementing and deploying a sensor network in an office setting.
The demonstration will show how to globally minimise and equalise the energy used for collaborative transmission.
Start/End: 2009-2011
Follow-ups: |
|
|
|
|
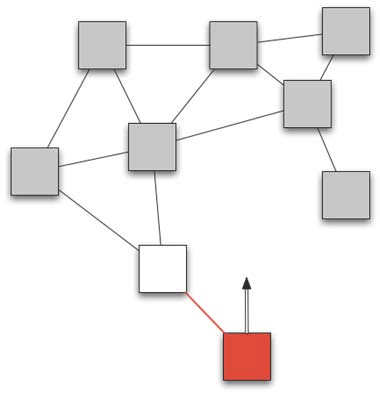  |
The aim of the project is to develop new methods for context prediction in wireless sensor networks and to utilise these for dynamic adaptation and optimisation of network behaviour.
Wireless sensor networks (WSN) provide the infrastructure for communication and measurement in environments where installing network and measurement hardware would be infeasible because of financial, local, and technical restrictions. Methods for prediction of time series are applied, for instance, in predicting financial time series or for computing weather forecasts.
Current approaches for prediction in WSNs estimate environment parameters to verify or correct measurement values. We apply methods of prediction to optimise parameters of the network.
The goal of the project SenseCast is to determine ways to anticipate critical situations in WSNs by applying methods of prediction and to dynamically optimise network properties and parameters accordingly. Thus, properties, such as reduced energy consumption and decreased latency, can be guaranteed. The focus of the project is to improve the quality of the prediction by decreasing the number of erros in the input time series, by employing collaborative strategies for prediction, and by optimisation of methods for context prognosis, as well as to utilise prediction strategies for adaptation of network parameters for optimisation of network behaviour in WSNs.
Start/End: 2009-2010
Research Topics: optimisation of context prediction in low-cost wireless sensor networks, collaborative strategies for context prediction, adaptation of network parameters based on prediction |
|
|
|
|
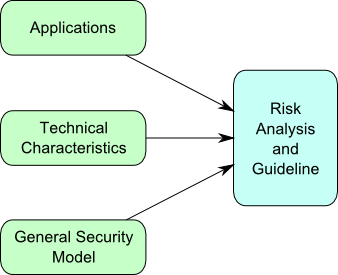  |
With the progress of wireless sensor network (WSN), this emerging technique is soon applied in many industrial projects. However, a standard to describe the security level in WSN is still lacking, which becomes very needful today. In MoSe Project we try to build a formal model to describe the security level of sensor network and also to give guideline of how to achieve these security levels. The work comprises following parts: collection of academic and industrial applications of WSN; building a formal characteristic card for WSN; investigating a formal model of security-related issues and the risk analysis with real examples.
Start/End: 2009-
Partners: ITM, Uni Karlsruhe Germany
Research Topics: Security of Sensor Networks, Survey of Applications/Technical characteristics of WSN
|
|
|
|
|
  |
Wireless sensor networks are well suited for supervising conditions in various environments.
When used in rail cargo for continuous monitoring of freight wagons, the results can provide many benefits for the operator,
such as train sequence monitoring, monitoring of unusual events that may lead to accidents or estimation of optimal service points.
The main challenges for WSNs in this scenario are an unfavorable radio channel as wagons are basically steel boxes as well as the requirement
of minimum to zero maintenance with sensor lifetimes of several years. The accurate monitoring of position and state of freight wagons
is a challenging application for wireless sensor networks (WSN). The owner of a freight wagon has limited impact on the exact travel route
or on the order and composition of wagons in a train. Wagons might be re-coupled several times before the final destination is reached and
wagons of several owners become mixed in trains. Therefore, an adaptive wireless solution is required.
The Projekt Intelligenter Güterwagon (PIG) is about evaluating the use of WSN technology in a freight train environment.
Before such benefits are available channel measurements have to be taken to find the basic operation conditions of a wireless sensor network (WSN),
and a WSN has to be designed, implemented and verified.
Start/End: 2009-2010
Partners: Particle-Computer , Novaconsult GmbH
Research Topics: Wireless sensor networks, Wake-up on radio, Ultra low power communication protocols
Follow-ups: |
|
|
|
|
  |
Classical approaches of computer science do not scale well for today's large and complex software-intensive systems. Software
systems cannot be considered in isolation, since they are connected among each other and interact massively. Instead they are to be designed as parts of a
larger IT Ecosystem. In analogy to biological ecosystems, IT Ecosystems are based on the balance between individuals (autonomy) and sets of rules (control)
defining equilibria within an IT Ecosystem. Maintaining and continuously evolving IT Ecosystems requires deep understanding of this balance.
In the IT Ecosystems subproject LocCom (local communities) we develop methods, concepts, and tools for decentralized IT Ecosystems. Our part is especially the
resaerch of context detection, handling and pattern recognition.
Start/End: 2009-2011
Partners: Technische Universität Clausthal, Leibniz Universität Hannover
Research Topics: Context detection and handling, pattern recognition
Follow-ups: |
|
|
|
|
  |
Chosen: Cooperative Hybrid Objects Sensor
Networks. Chosen researches, develops
and applies a ultra-low power standard
chipset for wireless sensor nodes that
will be SOA/Web2.0 enabled. The sensor
node will have features as wake-up-on-radio
pattern and will integrate directly into
Web 2.0 applications. Applications areas
cover automotive and avionics. TU Braunschweig
leads the middleware and system/integration
effort of this project.
Start/End: 2008-2011
Partners: Infineon,
TU
Vienna, Commissariat a l'Energie Atomique, EADS,
Fiat
Research Topics: Wireless sensor networks,
Web 2.0, SOA, Ubiquitous Computing applications,
ultra-low power
Application and economic dissemination:
standard wireless sensor platform, applications
in avionics, automotive
|
|
|
|
|
  |
SensorRAUM researches how to integrate and visualize sensor networks in virtual environments. The high density of sensor nodes respectively their sensors often lead to high cognitive load and prevent direct interaction with attached objects. The aim of SensorRAUM is to build 3D virtual environments for a better sensory perception which enable the interaction between real world and virtual world entities.
Start/End: 2007-
Partners: SAP, TecO, Particle Computer GmbH
Research Topics: 3D virtual environments, virtual world, virtual sensor reality, multi user dungeons, metaverses, reduction of cognitive load, presentability of sensor data
Application and economic dissemination: Prototype of virtual platform for ubiquitous applications, demonstrator
Follow-ups: |
|
|
|
|
  |
OSOITE: Overlay-network Search Oriented for Information about Town Events. OSOITE researches collaboration mechanisms of independent large scale sensor networks and how to improve user interaction with sensor data. Generally speaking people are likely to search things related to their daily lives in the real world ranging from straight-forward queries to complex ones. In order to expedite and realize the usage of sensor networks in ubiquitous society, sensor networks are expected to response to such real-world queries which is part of OSOITE.
Start/End: 2006-
Partners: Tokyo Denki University, University of Tokyo, Keio University, Chuo University, Fixstars
Research Topics: Distributed storage, real-world search, multi-resolution queries, interpolation, web API and query conversion, ease of deployment
Application and economic dissemination: Software kit and demonstrators
Sub-Projects: UScan |
|
|
|
|
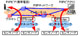  |
P2P4Ubicomp researches how to interconnect various distributed sensor networks, what performance measures are important, what and how information are replicated among involved remote locations etc. The project researches this issues regarding integrating into Internet and Telco environments and builds up large, world-spanning environments. Publication 1. Publication 2. Publication 3.
Start/End: 2006-
Partners: KDDI Research Japan, TecO
Research Topics: RFID system, RFID antenna, RFID based location detection, user behaviour recognition
Application and economic dissemination: Prototype, Used for supervising customer behaviour
Follow-ups: LoCostix |
|
|
|
|
  |
The goal of RELATE is to research in spatial relationships between tangible objects that together form an interface both in P2P location hardware, software (recognition, protocols, applications) and user applications. One goal of the project is to develop generic building blocks for a lightweight short range (room size) location system that does NOT require infrastructure, administration, configuration or management and can be integrated into everyday object. Another goal of the project is to research on potentials and use of such a novel type of location systems. More Information. Publication 1. Publication 2.
Start/End: 2003-2004, 2005-2008 (RELATE II)
Partners: Lancaster University, TU Delft, UMIT
Research Topics: infrared based location systems, ultrasonic based location systems, peer-to-peer location systems, real-time communication protocols, touchable interfaces, location aware applications
Application and economic dissemination: Prototype, applications
Follow-ups: |
|
|
|
|
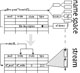  |
Tiny, ressource poor sensor nodes require novel operating systems concepts to perform appropriate, but also to present a application (and application developer) friendly interface. The project seeks to develop a micro-kernel, distributed operating system that provides UNIX-style API for programmers and represents all ressources as filesystems like ressources. Publication 1. Publication 2. Publication 3.
Start/End: 2005-
Partners: Hide Tokuda Lab, Keio University
Research Topics: operating systems, microkernel, file systems, distributed systems
Application and economic dissemination: Prototype
Follow-ups: |
|
|
|
|
  |
This project seeks to gather basic understanding in how far context aware camera systems are able to support human memory. The project seeks to develop a small wearable context aware camera device, gains insight into what activities are contributing to events we like to keep in memory, how to recognize these activities using a minimal set of sensors and computing power, how to present the memorized information and studies the use of such a system.
Start/End: 2005-
Research Topics: activity recognition, minimal hardware design, user studies,
Application and economic dissemination: Prototype
Follow-ups: |
|
|
|
|
  |
LoCostix develops basic technology and applications for ultra low-cost RFID systems to be used for item level tagging. The project addresses problems as antenna integration, packaging of RFID but also novel minimalized communication protocols and offset printed circuits (polymer electronics). The project seeks to prototype such innovative RFID systems while the run of the project, deploy them within warehouse environments (drug stores) and run application studies. Publication 1. Publication 2 .
Start/End: 2006-2009
Partners: TU Chemnitz, Philips GmbH, SAP Research, DM GmbH
Research Topics: RFID systems, novel minimized communication protocols, user and application studies
Application and economic dissemination: Prototype, deployment, product
Follow-ups: |
|
|
|
|
Superimposing RF Transmission |
|
|
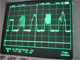  |
Superimposing codes can be used for a variety of applications in sensor network communication. One of the earliest applications was precise time synchronization of sensor nodes and channel access negotiation in AwareCon. More advances applications are using superimposed codes for ultra-fast ultra power-saving transmission of information - up to 1000 times faster than with traditional approaches. This builds the basis for novel ultra-minimized RF protocols, e.g. for novel types of RFID systems. It can also be used to extend reachability in sensor nodes (cooperative transmission) or using the radio channel to process information. More information. More information 2. Publication 1. Publication 2. Publication 3. Publication 4. Publication 5 . Publication 6.
Start/End: 2000-ongoing
Research Topics: Modulation schemes, superimposing radio waves, collaborative communication, inference modeling, radio propagation models, probabilistic estimation of data transmission, novel MAC protocols, minimal RF hardware design
Application and economic dissemination: basis for real time RF protocol (CoBIs, AwareCon, ...)
Follow-ups: LoCostix, CoBIs, RELATE |
|
|
|
|
  |
uParts are tiny little sensor network nodes that are very easy to deploy and run a 0-administration and low configuration (or 0-configuration when used with default) approach. The projects researches how to reach minimum deployment and maintenance costs of a sensor network and includes research on long lifetime hardware, 0-maintanance communication protocols, lower production costs and optimised application developer interfaces for ad-hoc programming. Application runs throughout the world provide feedback information that are evaluated in the project. More information. Publication 1. Publication 2.
Start/End: 2005-
Partners: Hide Tokuda Lab, Keio University
Research Topics: TCO for Sensor networks, ad-hoc programming for sensor network environments, communication protocols, application tests
Application and economic dissemination: Prototype, Used for several projects
Follow-ups: |
|
|
|
|
  |
The Smart Surroundings research program is investigating a new paradigm for bringing the flexibility of information technology to bear in every aspect of daily life. It foresees that people will be surrounded by deeply embedded and flexibly networked systems that provide easily accessible yet unobtrusive support for an open-ended range of activities, to enrich daily life and to increase productivity at work. This presents a paradigm shift from personal computing to ubiquitous computing , challenging the research community to investigate new building blocks and integrated infrastructures, as well as emerging applications and interaction styles. These systems will create a Smart Surrounding for people to facilitate and enrich daily life and increase productivity at work. These systems will be quite different from current computer systems, as they will be based on an unbounded set of hardware artefacts and software entities, embedded in everyday objects or realized as new types of device. Relevant knowledge areas include embedded systems, computer architecture, wireless communication, distributed computing, data and knowledge modeling, application platforms, human-computer interaction, industrial design, as well as application research in different settings and sectors. Our ambition is to move beyond prototypes toward sustainable systems for implementation of the ubiquitous computing vision. The research effort will span the entire spectrum ranging from scenarios of use, requirements elucidation and through to architectural design. More information.
Start/End: 2004-2007
Partners: University of Twente, Lancaster University, TU Delft, Philips,
TNO, Nedap, Roessingh Research, Thales, TalkingHOME, Océ
Research Topics:
embedded systems, computer architecture, wireless communication, distributed computing, data and knowledge modeling, application platforms, human-computer interaction, application research
Application and economic dissemination: Prototype, Used for supervising customer behaviour
Follow-ups: |
|
|
|
|
  |
CoBIs develops a radically new approach to business processes that concerns physical entities in enterprise environments (goods, tools, etc). This approach embraces advances in networked embedded systems to embed business logic in the physical entities, thereby creating Collaborative Business Items (CoBIs). These items bring closer together the state of an enterprise as represented in a business process with what is actually happening in the real world. The intention of CoBIs is to apply advances in Networked Embedded Systems to embed business logic in the physical entities to create Collaborative Business Items that make it possible to relate more closely the state of an enterprise as represented in a business process with what is actually happening in the real world. More Information 1. More Information 2. More Information 3. More Information 4. Publication 1.
Start/End: 2004-2007
Partners: SAP Research, Lancaster University, Infineon AG, BP, University of Twente
Research Topics: Integrating Sensor Systems and Enterprise Systems: Interface definition, process exchange language, mobile code, collaborative activity. Operating system: mobile codes sensor networks. Communication: Real-time communication system (AwareCom), Service Interfaces for Sensor Networks. Hardware: Shock, Chemical robust HW, Application Studies: Use of sensor networks in highly sensitive environments
Application and economic dissemination: Prototype, Deployment at BP in Hull/UK
Follow-ups: Particle-Computer GmbH (Start-Up) |
|
|
|
|
  |
AwareOffice researches deployment and of Ubiquitous Computing technology in office settings. One aspect is the embedding of sensor nodes into everyday objects, integration of novel types of devices (e.g. electronic doorplates) and developing hardware, libraries and software for running a office of the future. Other aspects are collection of sensor data an activity monitoring, or user behaviour recognition in general. The project provides also a test-bed platform for other projects (Smart-Its, RELATE, CoBIs, LoCostix). More Information.
Start/End: 2003-
Partners: SAP Research
Research Topics: sensor node hardware, development of novel user interface devices, integration of consumer electronics, acclivity recognition and context awareness, user studies
Application and economic dissemination: Prototype, test bed
Follow-ups: |
|
|
|
|
  |
ContextAsAKey is an approach to reach ad-hoc security and privacy in a Ubiquitous Computing environment without any user involvement - management, configuration nor administration. The basic principle is the use of the common context that exist when computing devices are located close to each other in the same physical environment. Technically the system bases on advanced transformation and recognition methods which are used to compare sensor patterns received by sensors on embedded sensor nodes. Publication 1.
Start/End: 2004-
Research Topics: sensor pattern recognition, sensor pattern comparison
Application and economic dissemination: Prototype
Follow-ups: |
|
|
|
|
  |
Particle Computer is an enabling platform for various scenarios related to Ubicomp. Particles are tiny wireless nodes where a huge variety of sensors can be attached. Further, the fully programmable micro controller accompanied by powerful libraries let novices as well as professionals implement applications in the fields of sensor networks, human-computer interaction, supply-chain management and many more. The proprietary communication protocol AwareCon is able to handle highly mobile and highly scalable communication situations. Although battery-driven, Particle Computer can achieve lifetime of up to several years. The project covers several aspects including system software and tools for developing Particle applications and sensor data analysis. More information. Publication 1. Publication 2. Publication 3.
Start/End: 2004-
Partners: TecO
Research Topics: Sensor node hardware, Sensor node firmware, low-power communication protocols, sensor node system software and OS,
Application and economic dissemination: Prototype, Used for almost all projects since 2004, Spin-off Particle-Computer GmbH
Follow-ups: LoCostix, RELATE, P2P4Ubicomp, CoBIs, SmartSurroundings |
|
|
|
|
  |
The MediaCup is an ordinary coffee cup augmented with sensing, processing and communication capabilities (integrated in the cup's bottom), to collect and communicate general context information in a given environment. It is an example how to equip everyday objects with computing and communication capabilities. With the MediaCup setup (consisting of several cups and other equipment) we explored the added value of computerized everyday objects. The projects develops a proprietary ultra-low power infrared based communication system, a location aware routing mechanism, a hybrid location system and gains insight to user behaviour of everyday objects performing various studies. More Information . Publication 1. Publication 2. Publication 3. Publication 4. Publication 5.
Start/End: 1998-2005
Research Topics: Activity recognition, Location models, location systems, ultra-low-power hardware, embedded interaction, user studies in Ubicomp environments, location aware communication protocols
Application and economic dissemination: Prototype
Follow-ups: Smart-Its, RELATE |
|
|
|
|
  |
Rather than using a hierachical approach to resolve RFIDs indentification code to database information this project researches in using Peer-to-Peer technology. The project showed that privacy of information can be better ensured and higher reliability can be gained using such an approach Publication 1.
Start/End: 2003
Research Topics: RFID resolving service, P2P systems
Application and economic dissemination: Prototype
Follow-ups: Locostix, P2P4Ubicomp |
|
|
|
|
  |
The Smart-Its project is interested in a far-reaching vision of computation embedded in the world. In this vision, mundane everyday artefacts become augmented as soft media, able to enter into dynamic digital relationships. In our project, we approach this vision with development of "Smart-Its" - small-scale embedded devices that can be attached to everyday objects to augment them with sensing, perception, computation, and communication. "Smart-Its" is enabling technology for building and testing ubiquitous computing scenarios, and we will use them to study emerging functionality and collective context-awareness of information artefacts. While the Smart-Its several types of wireless sensor nodes where build, communication protocols, applications are developed and and user studies performed. More Information. Publication 1. Publication 2. Publication 3. Publication 4. Publication 5. Publication 6. Publication 7. Publication 8. Publication 9.
Start/End: 2000-2003
Partners: Lancaster University, ETH Zürich, Interactive Institute, VTT (EU Funded project)
Research Topics: Ubiquitous Computing, wireless sensor nodes hardware, wireless sensor networks, OS for wireless sensor nodes, sensor & context library, context recognition, user studies, applications, distributed awareness, context proximity
Application and economic dissemination: Prototype
Follow-ups: Particle-Computer GmbH (Start-Up), RELATE, CoBIs, AwareOffice, superimposed Transmission |
|
|
|
|
  |
AwareCon is an approach for communicating in context aware environments and the network stack for the Particle Computers. AwareCon goes beyond traditional network approaches by using sensed context information from the environment to adjust parameters inside the network stack and by optimising the transfer of context information inside Ubiquitous Computing environments. It is therefore both context aware because it uses context information (from own sensors or by being informed from other devices in the environment) to gain performance (in terms of latency, power consumption, real-time behaviour) and it is context aware because it transferees context information. AwareCon consists of two main layers: A lower layer dealing with performance optimised transfer and a higher layer (ConCom) dealing with context information transfer and context description ontology. AwareCon is the network stack used for all pPart Particle Computers. Publication 1.
Start/End: 2002-
Research Topics: Network and communication (all layers), Context aware systems
Application and economic dissemination: Implemented in AwareCon for Particle Computer GmbH
Follow-ups: |
|
|
|
|
  |
The eSeal concept researches how to extend the concept of seals to general objects using Ubiquitous Computing technology. It identifies which additional threads can be detected using an electronic seal an implements several prototype seals. A major implementation path of eSeal was the DigiClip. The DigiClip system allows the tracking, synchronization and and integrity control of paper-based documents with their electronic counterparts. Particles were integrated in a paper clip and allowed to obtain location information for a document. In conjunction with a document management system, the DigiClip device enabled a physical notification of changes of the electronic document. The sensors of the DigiClip device allow further the application of integrity rules on the physical document, such as document integrity on a single page-level, handling constraints and location restrictions. The DigiClip device hardware was built by the Adam Eames from MIT who did an internship at SAP at this time. More Information. Publication 1. Publication 2.
Start/End: 2004-2005
Partners: SAP AG, MIT
Research Topics: Novel sensor hardware, Novel sensor recognition software, sensor nodes, Enterprise systems to sensor network integration
Application and economic dissemination: Prototype, application tests
Follow-ups: CoBIs |
|
|
|
|
  |
ParticleBasic simplifies the programming of sensor nodes and enables rapid prototyping of applications. It consists of two major components: A small scale VM on the Particle Computer and an interpreter running on top of it and a compiler for the development platform (written in JAVA) that generates byte code for the VM. An additional small helper application simplifies the upload of the byte code to the Particle. More information.
Start/End: 2004
Partners: GeorgiaTech
Research Topics: Ad-hoc programming, programming environments, VM
Application and economic dissemination: VM and Compiler for Particle Computer
Follow-ups: |
|
|
|
|
  |
The In/Out Board is an ambient display showing the presence of persons in an office environment based on their activity. It integrates recognition of persons using RFID technology and PC based background services with an ambient display.
Start/End: 2004
Partners: SAP AG
Research Topics: RFID system, Integration of information infrastructure
Application and economic dissemination: Implementation running at SAP research
Follow-ups: |
|
|
|
|
  |
SmartShelf develops basic technology and a demonstrator. It shows how RFID technology can be used to locate objects on a shelf. The SmartShelf is able to be aware of goods standing on top of the shelf and detects the individual fine-grained position of each object. It is also able to recognize activities performed with the objects and can conclude on the the customers behaviour. Applications are customer customer behaviour recognition and retail store inventory applications.
SmartShelf also allows to research various strategies to understand and influence the
customers' decision behaviour during the process of buying items in a
retail store. The SmartShelf is a technology to reveal customers'
interactions with a product item in an unobtrusive way. This opens up a
huge potential for applications. These include recommender systems
similar to that known form amazon, but situated in real world retail
stores, plan-o-gram compliance applications, out-of-stock predictions
and theft prevention. Analysis of advertisement campaigns and product
bundling
were also a target areas. More Information. Publication 1. Publication 2.
Start/End: 2002
Partners: SAP AG
Research Topics: RFID system, RFID antenna, RFID based location detection, user behaviour recognition
Application and economic dissemination: Prototype, Used for supervising customer behaviour
Follow-ups: LoCostix |
|
|
|
|
  |
RAUM is a communication principle for spontaneous communication between small devices in Ubiquitous Computing environments. Its central idea is to use location information to assign producers and consumers of communication events in such environment and provide location aware and location dependent routing to distribute information within Ubiquitous Computing environments. The centre of the RAUM system consists of a hybrid (geometric and semantic or symbolic) location model for describing indoor locations and a location aware, subscription driven routing algorithm. Publication 1. Publication 2. Publication 3.
Start/End: 1997-2002
Research Topics: hybrid location model, geometric location model, location aware routing
Application and economic dissemination: Prototype
Follow-ups: AwareCon |
|
|
|
|
  |
AmbientTelepresence researched the possibility to build up a ambient presence of remote people using a Ubiquitous Computing environment instrumented with embedded devices rather than with video or audio transmission. "Ambient Telepresence is a method to give someone the feeling that someone else is present while they
are not co-located". The project showed that transfer of (selected) ambient events are less obtrusive and allows for a more fine grained, continuous awareness of remote persons. Technically the prototype connects remote sites using the events from the MediaCup and consumer electronics and reproduces an ambient awareness using sound. More information. Publication 1. Publication 2.
Start/End: 2000
Research Topics: CSCW, ambient awareness, user studies
Application and economic dissemination: Prototype
Follow-ups:
|
|
|
|
|
  |
Reminder tools allow users to associate information with time-based alarms. However, in many cases space rather than time may be appropriate to trigger reminders. A wearable artifact, the MemoClip (a small clip), reminds a user of things he should do depending on where he is. A user can associate information to be remembered with a description of a location, download it onto the MemoClip, and then gets notified accordingly when entering the selected location. The project researches how user can be reduce cognitive load using novel types of reminder systems and researches selected topics of hardware and communication protocols - namely ultra-low power location beacons and location beacon communication protocols. More information 1. More information 2. More information 3. Publication 1.
Start/End: 1999-2000
Research Topics: Reminder applications, low-power location beacon hardware, low-power location beacon communication protocols
Application and economic dissemination: Prototype
Follow-ups: MemCam |
|
|
|
|
  |
Several projects reserched the use of ambient, non-obtrusive human-computer interaction. For wearable computers, we developed an interface that is able to observe users behaviour and conclude on the behaviour (implicit Human Computer Interaction). In contrast to traditional HCI concepts, users have not to be trained for the application nor have do they need to be aware of the computer. Applications of this where used to automatic trigger processes in an electronic business workflow based on a users activity. With the WearablePacketReader demonstrator we showed that there is economic merit using such technology. Other applications are used to automatically trigger configurations based on detected activity or how to build non-obtrusive interfaces using HMDs. Publication 1. Publication 2. Publication 3. Publication 4.
Start/End: 1999-2002
Partners: SAP AG
Research Topics: Implicit Human Computer Interaction, Ambient Computing, Ambient Human Computer Interaction, Wearable Computing, Augmented Reality
Follow-ups: |
|
|
|
|
  |
Point&click researches on ways to control devices in the environment using a single handheld device and interface. It concludes that a split in two phases (point and click) is most appropriate also for controlling (embedded) electronic devices in a physical environment. It also found that there is less chance to find a general interface for presenting control to the user and concludes that devices must download control information to the controlling device - but in a structured matter so that differences between various devices are kept minimal. The system approach should follow a 3-step process before interaction (point, click, download). The Point&Click prototype implements a 5 button 1-hand usable small handheld computing interface device that demonstrates the found usability principles. More information.
Start/End: 1999
Research Topics: Interaction design for Ubiquitous Computing environments
Application and economic dissemination: Prototype
Follow-ups: UbicompBrowser, ElectronicManual |
|
|
|
|
  |
UbicompBrowser researches how electronic consumer devices embedded into the environment can be connected to the information network using Internet technologies. It results in a prototype that is able to bridge the gap between physical devices and information space by utilizing a handheld device equipped with a Barcode scanner - the UbicompBrowser. Using the UbicompBrowser software a user is able to control the device by first identifying the device and then controlling the device in a proprietary way using a software downloaded from the site of the device producer. The ElectronicManual extends this idea by integrating manual and helping information into the usage of electronic consumer devices. More information. Publication 1.
Start/End: 1998-1999
Research Topics: Ubiquitous Computing environments appliances, Interaction design, Ubiquitous system design, Interaction design, Usage studies
Application and economic dissemination: Prototypes
Follow-ups: Point & Click |
|
|
|
|
|